Technical Information

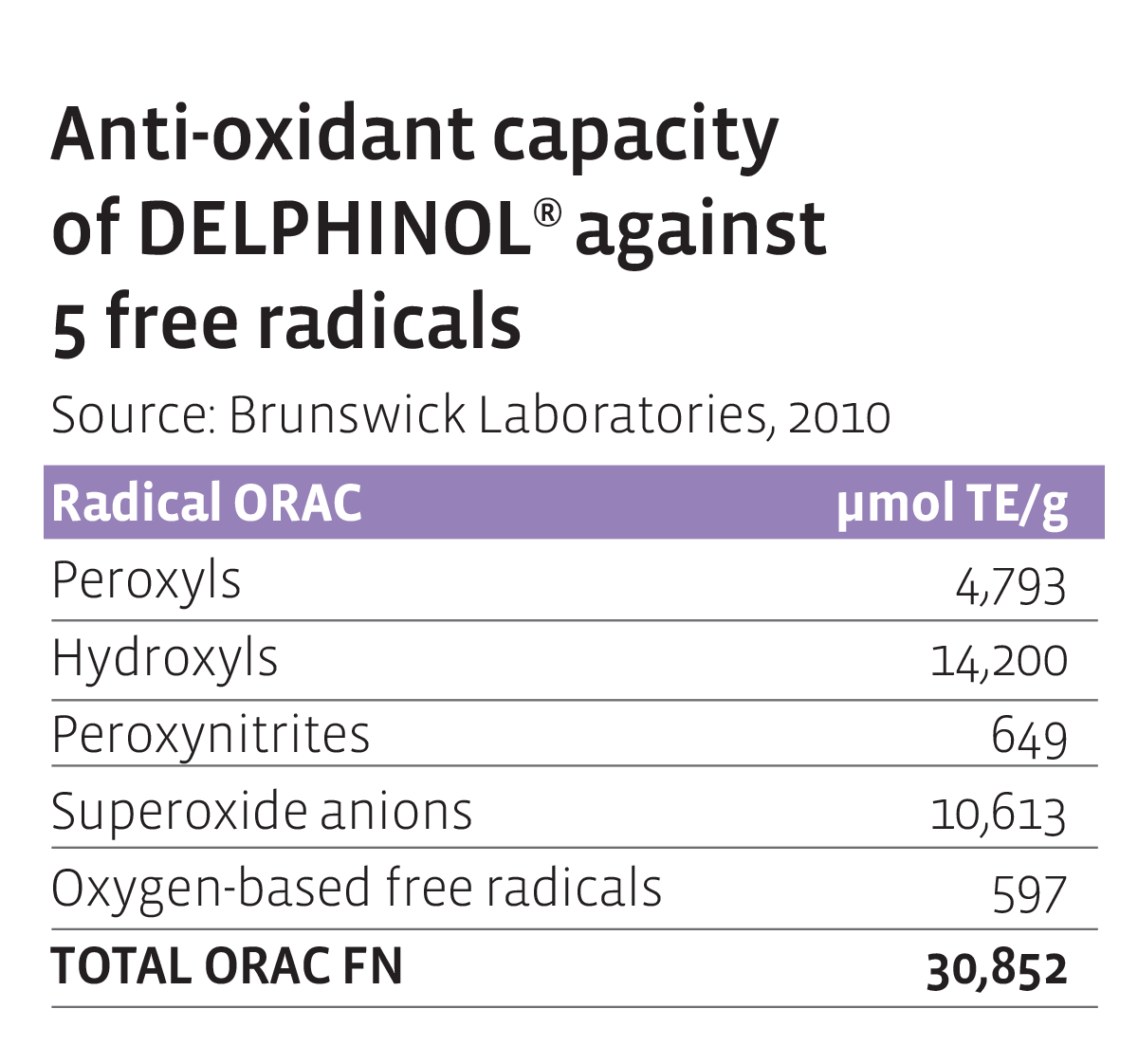
ORAC
The acronym ORAC comes from the phrase Oxygen Radical Absorbance Capacity.
It gives an account of the overall activity or capacity that all of the antioxidants present in a food product (or other sample) have to “turn off or neutralize” free radicals that are the result of oxidative stress; the higher the ORAC rating gets, the more powerful the antioxidant activity of the food item becomes.
Oxidative Stress
This is a biological condition where the speed at which different pro-oxidant species are generated (free radicals) is greater than the speed at which these species are neutralized. Low levels of antioxidants or the inhibition of antioxidant enzymes cause oxidative stress and can cause damage to or kill cells. Oxidative stress has been associated with the pathogenesis of many human diseases.
Free Radicals
There are a number of “free radicals” that operate in human beings. The most important of these are hydroxyl, peroxyl, peroxynitrite, atomic oxygen, and super oxide anion radicals. It is important to protect our bodies from all of these harmful radicals because they contribute to “oxidative stress.”
THE 5 FREE RADICALS THAT ARE CONSIDERED TO BE THE MOST REACTIVE ARE:
PEROXYL RADICAL
HYDROXYL RADICAL
This radical is highly reactive and cannot be eliminated by our endogenous enzymes. Hydroxyl radicals are created in the skin through UV exposure.
SUPER OXIDE ANION
This is the precursor to all of the other reactive oxygen species and considered to be the “mother of free radicals.” It is highly toxic and contributes to the damage of lipids and cellular DNA. The antioxidants that clean super oxide anions also help to prevent the formation of radicals such as hydrogen peroxide and hydroxyl. Super oxide anions have been linked to hypertension and cardiovascular damage.
SINGLET OXYGEN
This radical is linked to the oxidation of LDL cholesterol and cardiovascular diseases.
PEROXYNITRITE
This is a species of reactive nitrogen derived from the super oxide anion which is particularly harmful to proteins. It is linked to the development of certain types of cancer, hepatitis, and chronic inflammations.

Polyphenols and Flavonoids
These compounds are biosynthesized by plants (their fruits, leaf tissue, stems, roots, seeds, or other parts of the plant). All polyphenols display antioxidant properties.
These compounds give an account of a great part of the antioxidant activity that is exhibited by fruits, vegetables, and certain infusions and natural drinks regularly consumed by the population.
It is also possible to identify subtypes of the compounds among the polyphenols; flavonoids are also divided into 5 groups: anthocyanins, flavonols, flavanones, flavones, and isoflavones
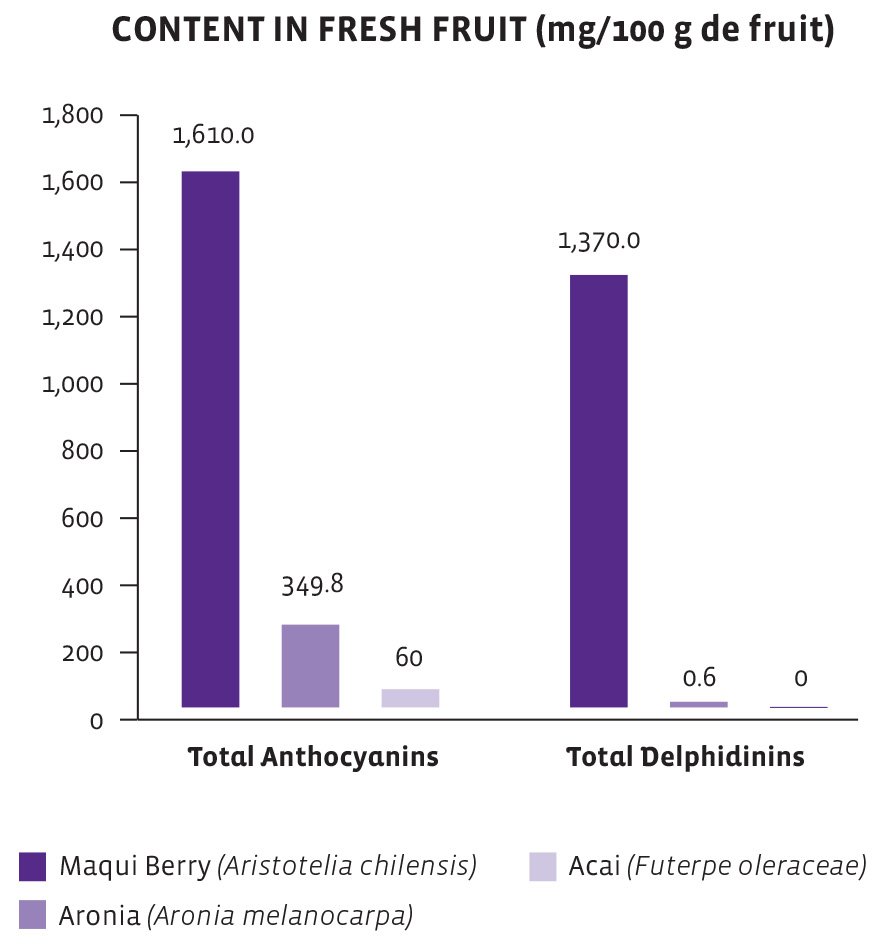
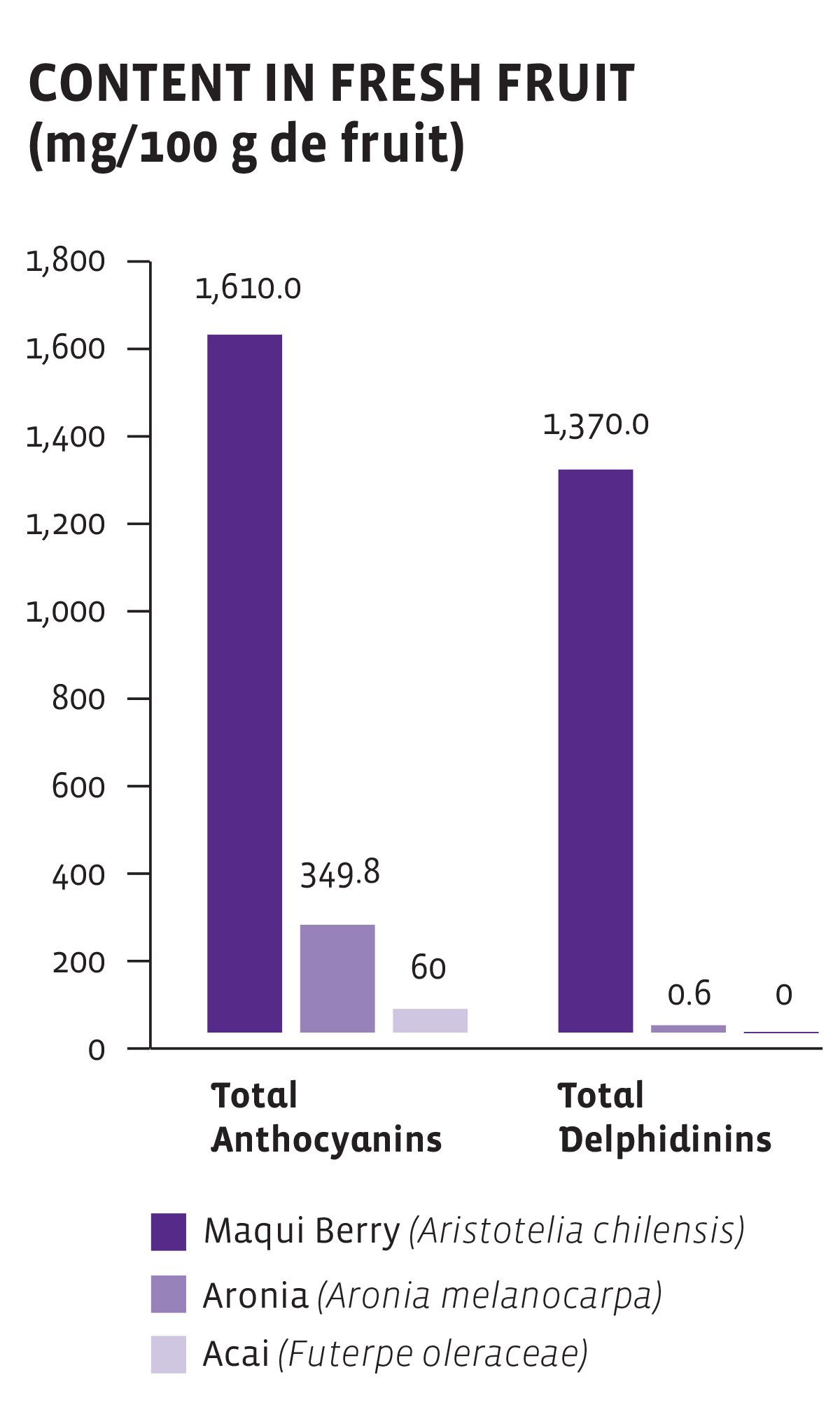
Anthocyanins and Delphinidins
What are anthocyanins and delphinidins?
Anthocyanins are polyphenols with antioxidant activity that are considered to be biologically beneficial to human health. Delphinidins are anthocyanins, one of the primary pigments of plants, and are also antioxidants.